Indian Journal of Health Social Work
(UGC Care List Journal)
PSYCHOLOGICAL MINDEDNESS AND SOCIAL FUNCTIONING OF INDIVIDUALS WITH ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE SYNDROME: A COMPARATIVE STUDY
Muhammed Sadik T.M1& Shuvabrata Poddar21Ph.D Scholar (Department of Applied Psychology, Kazi Nazrul University) Asansol, and Assistant Professor ( Department of Clinical Psychology, Central Institute of Psychiatry), Kanke, Ranchi. 2Assistant Professor, Department of Applied Psychology, Kazi Nazrul University, Asansol,.
Correspondence: Muhammed Sadik T.M, e-mail: sdk.alt@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Background: Alcohol abuse is a major public health concern. Various biological, psychological, and social determinants are there in the well-being of an individual. Aim: The present study aims to assess the impact of psychological mindedness and social functioning on the well-being of patients with alcohol dependence syndrome. Method & Materials: 30 individuals with Alcohol Dependence Syndrome and healthy normal were selected through purposive sampling. Wellbeing was assessed using the Psychological Mindedness Scale and Social and Occupational Assessment Scale among both groups and statistical operations were done using the Independent Sample t test and Pearson Correlation Coefficient . Results & Conclusion: Studt suggest that significant differences were observed in terms of psychological mindedness and social functioning. It was concluded that the well being is negatively affected due to less psychologically minded and difficulty in social functioning. Further a holistic approach can be done to improve the wellbeing.Keywords: Alcohol, psychological mindedness, social functioning, well being
INTRODUCTION
Well-being can be described in terms of an individual’s condition concerning the psychological, social, and biological basis. It has been defined the health as “the full physical, mental and social well being not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO, 2001). Various determinants are there in the well-being framework, One among them is interpersonal relationships. It has been studied that the well-being of individual is affected due to the consumption of alcohol despite the pattern of drinking ( Nguyen & Cairney, 2013). Consumption of alcohol among the young adults has been a complex phenomenon, which is deeply interconnected with biological, psychological, social and cultural factors. It plays a major in the lives of adults in the world wide such as a celebrating agent to coping agent. In many cultures across the world, consumption of alcohol is acceptable socially. social or experimental phase of consumption is leading to have less consequences but abusive to dependence phase of consumption lead to have destructive consequences in the individual. Severe pattern of consumption of alcohol results major consequences. In the medical background, it has been studied that excessive consumption of alcohol lead to have a destructive consequence and which could be a life threatening (Clark et. al., 2001) The social ground has been destructive due to the excessive consumption of alcohol and that might lead to have significant distress in the individual (Vinader-Caerols, 2014). It is severely affected in occupational phase of the individual in terms of increased absenteeism; where they are on sick leave and shows less interest in the work and more interest in consumption of alcohol. Work related accidents, less productivity at work and difficulty in maintaining healthy relationship with colleagues and which may further result in unemployment due to excessive drinking ( MacDonald and Shields, 2001) . It has been observed that the mindset of individuals struggling with alcoholism fluctuate widely. They experience a sense of distress where a preoccupied thoughts of drinking alcohol dominate their mental space. Substance addiction is a chronic, relapsing brain disease that is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences(National Institute on Drug Abuse, 2007). The social ground has been destructive due to the excessive consumption of alcohol and that might lead to have significant distress in the individual. Where the individual faces a difficulty in understanding the perspectives of others (Gustafson, 1988). Psychological mindedness defines as an individual’s ability to understand one’s own and other’s mental processes. It can be further explained as Willingness to try to understand oneself and others, openness to new ideas and capacity to change, access to feelings, belief in the benefits of discussing one’s problems, and interest in meanings and motivation of own and others’ behavior Shill and Lumley (2002). The purpose of the current case study is probe into the impact of social functioning, severity of addiction and psychological mindedness on the well being of individual with alcohol dependence syndrome.OBJECTIVE
To assess the impact of psychological mindedness and social functioning on the wellbeing of patients with alcohol dependence syndrome.METHODS & MATERIALS
Sample: Male Participants were selected randomly from a de-addiction centre of south part of India. There were 30 participants with the Alcohol Dependence Syndrome and 30 healthy normal controls. The age range of the patient was between 25-35 years with the minimum education of 8th std. The patient is having less than 2 years of dependence comorbid substance abuse history, other comorbid psychiatric disorders, mental retardation and organic history were excluded.Assessments: Socio-demographic and Clinical Data Sheet was used for the information about socio-demographic variables like age, education, residence, occupation and clinical variables like age of onset of illness, duration of illness. Psychological Mindedness Scale (Conte et al., 1996), a 45- item self-report instrument with items rated on a 4-point was used for assessing the psychological mindedness. The Social and Occupational Functioning Assessment Scale (Morosini, 2004) was used to assess the routine functioning. And Severity of Alcohol Dependence Scale (SADQ) by Stockwell (1983), 20-item questionnaire, was used to assess the severity of the dependence.
Procedure: 30 participants with Alcohol dependence and healthy normal controls were taken. The assessments included Sociodemographic profile, Psychological Mindedness Scale, The Social Occupational Functioning Scale, and Severity of Alcohol Dependence Questionnaire.
RESULTS
The present chapter gives the results of the analysis of the data of the present study. The data analysis was done using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS-27.0 Version) software.
Table-1.1 shows the comparison of the two groups in their conitnous variables by using Independent sample t test method. This shows that the two groups did not differ significantly in the following variables assessed.
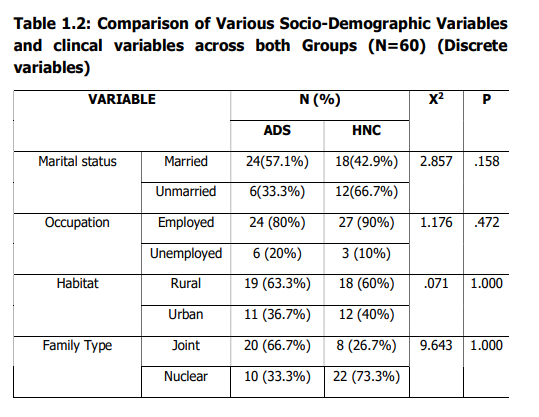
Table 1.2 shows the pearson chi-square was
used to compare the discrete variables. With
This shows that the two groups did not differ
significantly in the following variables
assessed.
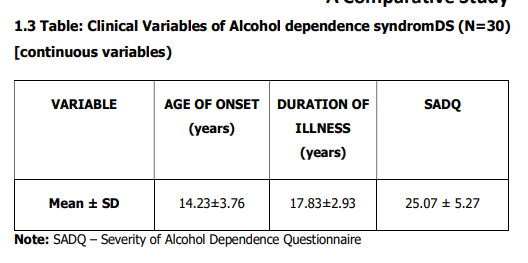
The 1.3 Table shows the mean ranges of age
of onset, duration of illness and severity of
alcohol dependence. This explains that patient
with alcohol dependence have moderate level
of dependence.

Table 2 shows that shows the comparison of
the scores of socio and occupational
functioning, psychological mindedness and
mentalization between patients of alcohol
dependence syndrome and healthy normal
controls using independent sample ‘t’ test.
Both group showed a significant difference in
the scores of social and occupational
functioning (P d” 0.01) and psychological
mindedness (P d” 0.01). with regards to the
scores of domains os mentalization, both
group did not differ significantly.
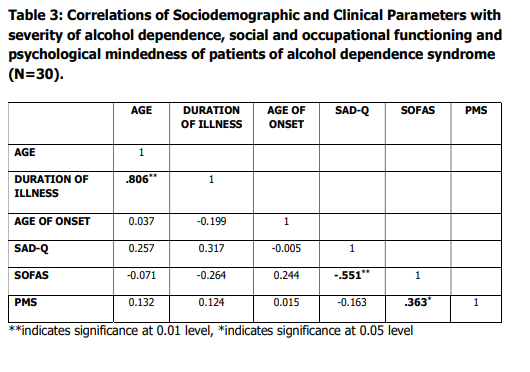
Table 3.: shows the pearson’s correlations of
Sociodemographic and Clinical Parameters with severity of alcohol dependence, social
and occupational functioning and psychological
mindedness of patients of alcohol dependence
syndrome. There is significant positive
correlation between the age and duration of
illness ( r=.806**), indicating that as the age
increases the duration of illness of also
increases. Psychological mindendness is
significantly correlated positively with social
and occupational functioning ( r=.363**). This
suggests that the more they are
psychologically minded the more they are able
to be involved in social and occupational
functioning. Further, severity of alcohol
dependence is significantly correlated
negatively with social and occupational
functioning ( r=.363**).
DISCUSSION
The present study showed that there are young adults who have developed alcohol dependence and their overall well-being is affected. It has been noted in the study that the age which the patients started consuming alcohol is adolescents ( Mean of 14.23±3.76). in the current scenario, the prevalence of alcohol consumption in India is about 20 % of adolescents aged 15 to 19 years (Kumar et al., 2016). A significant difference (p= .019*) was found in religion among both group. The present study also showed that the patients with alcohol dependence ( 63.93±9.850) have more problem in social and occupational functioning than controls ( 88.33±3.889). this could be due to that alcoholics show significant impairment in social and occupational functioning. It affects their interpersonal relationships, emotional regulation, productivity of the job, increases the absenteeism and mainly performance of cognition. Similar study has noted that severity of alcohol dependents affects their social functioning. Also, it resulted that as the stigma which are internalized regarding the illness increases about their, social functioning decreases ( Arabaci, 2020). Alcohol dependents seem to be less psychologically minded than healthy normal. This states that the difficulty to understand the mental process of them as well as others. It was also studied that social and occupational functioning was significantly correlated positively with psychological mindedness (r= .363* ) and negatively with severity of alcohol dependence (r= -.551** ). This can be further explained as the more they are psychologically minded, the more they are able focus on their social and occupational functioning. Ferrer and Marks (2016) studied that the more the person is aware about their psychological processes, lesser the chance to develop the dependence in alcohol. This was reasoned to assume that those with higher awareness of the self are more able to execute their cognitive functioning and further it helps to prevent them from excessive consumption of alcohol. The severity of dependence increases impairment in interpersonal relationship, communication, mental processes, and work related issues such as difficulty in engaging in their duty, co-operative atmosphere with co-workers. In this study, individuals with alcohol dependence are less psychologically minded. This may create a difficulty in being open to new ideas and capacity to change, accessing to feelings and understanding about themselves and others. They face hurdles in dealing with daily life that may be affecting their social sphere and occupational space. They fail to have an adequate interpersonal relationship, communication, good performance at their work place. Due to this, the well being is affected and results in experiencing severe psychological distress. And Cecero, Beitel, and Prout (2008) studied the psychological mindedness can be seen as an increment in coping skills and reduction in the distress. Further, the present study indicated that patients with alcohol dependence who are less minded, the coping mechanism is affected, that may lead to them engaging in substance seeking behaviour as a part of coping.
The present study showed that there are young adults who have developed alcohol dependence and their overall well-being is affected. It has been noted in the study that the age which the patients started consuming alcohol is adolescents ( Mean of 14.23±3.76). in the current scenario, the prevalence of alcohol consumption in India is about 20 % of adolescents aged 15 to 19 years (Kumar et al., 2016). A significant difference (p= .019*) was found in religion among both group. The present study also showed that the patients with alcohol dependence ( 63.93±9.850) have more problem in social and occupational functioning than controls ( 88.33±3.889). this could be due to that alcoholics show significant impairment in social and occupational functioning. It affects their interpersonal relationships, emotional regulation, productivity of the job, increases the absenteeism and mainly performance of cognition. Similar study has noted that severity of alcohol dependents affects their social functioning. Also, it resulted that as the stigma which are internalized regarding the illness increases about their, social functioning decreases ( Arabaci, 2020). Alcohol dependents seem to be less psychologically minded than healthy normal. This states that the difficulty to understand the mental process of them as well as others. It was also studied that social and occupational functioning was significantly correlated positively with psychological mindedness (r= .363* ) and negatively with severity of alcohol dependence (r= -.551** ). This can be further explained as the more they are psychologically minded, the more they are able focus on their social and occupational functioning. Ferrer and Marks (2016) studied that the more the person is aware about their psychological processes, lesser the chance to develop the dependence in alcohol. This was reasoned to assume that those with higher awareness of the self are more able to execute their cognitive functioning and further it helps to prevent them from excessive consumption of alcohol. The severity of dependence increases impairment in interpersonal relationship, communication, mental processes, and work related issues such as difficulty in engaging in their duty, co-operative atmosphere with co-workers. In this study, individuals with alcohol dependence are less psychologically minded. This may create a difficulty in being open to new ideas and capacity to change, accessing to feelings and understanding about themselves and others. They face hurdles in dealing with daily life that may be affecting their social sphere and occupational space. They fail to have an adequate interpersonal relationship, communication, good performance at their work place. Due to this, the well being is affected and results in experiencing severe psychological distress. And Cecero, Beitel, and Prout (2008) studied the psychological mindedness can be seen as an increment in coping skills and reduction in the distress. Further, the present study indicated that patients with alcohol dependence who are less minded, the coping mechanism is affected, that may lead to them engaging in substance seeking behaviour as a part of coping.
CONCLUSION
This study highlights that patients with severity of alcohol dependents lead to have difficulty to be minded of their own mental processes and profoundly impaired social and occupational functioning. The well being is negatively affected due to their strained interpersonal relationships, communication, increased absenteeism and less productivity. A holistic approach can be done to improve the well being of the patients with alcohol dependents using the influence of psychological state, reducing alcohol seeking behavior and social and occupational functioning.
This study highlights that patients with severity of alcohol dependents lead to have difficulty to be minded of their own mental processes and profoundly impaired social and occupational functioning. The well being is negatively affected due to their strained interpersonal relationships, communication, increased absenteeism and less productivity. A holistic approach can be done to improve the well being of the patients with alcohol dependents using the influence of psychological state, reducing alcohol seeking behavior and social and occupational functioning.
LIMITATION
The present study is limited to only 60 participants that may not be giving a adequate representation of the cohort with alcohol dependence syndrome. And, the study focused on only male participants and that may suppresses the general applicability of the findings to the other genders.
The present study is limited to only 60 participants that may not be giving a adequate representation of the cohort with alcohol dependence syndrome. And, the study focused on only male participants and that may suppresses the general applicability of the findings to the other genders.
REFERENCES
Arabaci, L. B., Dagli, D. A., Tas, G., & Arslan,
A. B. (2020). Stigmatization and social
functioning levels of patients with
alcohol use disorders. Journal of
Addictions Nursing, 31(4), 295-301.
Cecero, J.J., Beitel, M. and Prout, T., 2008,
Exploring the relationships among
early maladaptive schemas,
psychological mindedness (PM) upon
the relationship between early
maladaptive schemas (EMS) and selfreported college adjustment.
Psychology and Psychotherapy:
Theory, Research, and Practice, 8,
105-118.
Clark, D. B., Lynch, K. G., Donovan, J. E., &
Block, G. D. (2001). Health problems
in adolescents with alcohol use
disorders: self report, liver injury, and
physical examination findings and
correlates. Alcoholism: Clinical and
Experimental Research, 25(9), 1350-
1359.
Conte, H. R., Ratto, R., & Karasu, T. B. (1996).
The Psychological Mindedness Scale:
Factor structure and relationship to
outcome of psychotherapy. The
Journal of psychotherapy practice and
research, 5(3), 250.
Ferrer, E., & Marks, R. (2016). Predicting
alcohol use in a cohort of college
students based on psychological
mindedness, counseling, and
demographic variables. International
Journal of Psychology and Behavioral
Sciences, 6(2), 39-46.
Kumar, V., Kumar, D., Shora, T. N., Dewan, D.,
Mengi, V., & Razaq, M. (2016).
Prevalence of tobacco, alcohol, and
other drug abuse among school-going
male adolescents in
Jammu. International Journal of
Medical Science and Public
Health, 1(5), 246-51.
MacDonald, Z., & Shields, M. A. (2001). The
impact of alcohol consumption on
occupational attainment in England.
Economica, 68(271), 427-453.
Morosini, P. L., Magliano, L., Brambilla, L. A.,
Ugolini, S., & Pioli, R. (2000).
Development, reliability and
acceptability of a new version of the
DSM IV Social and Occupational
Functioning Assessment Scale
(SOFAS) to assess routine social
funtioning. Acta Psychiatrica
Scandinavica, 101(4), 323-329 Nguyen, O. K., & Cairney, S. (2013). Literature
review of the interplay between
education, employment, health and
wellbeing for Aboriginal and Torres
Strait Islander people in remote
areas.
Shill, M. A., & Lumley, M. A. (2002). The
Psychological Mindedness Scale:
Factor structure, convergent validity
and gender in a non psychiatric
sample. Psychology and
Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and
Practice, 75(2), 131-150.
Stockwell, T., Murphy, D., & Hodgson, R.
(1983). The severity of alcohol
dependence questionnaire: its use,
reliability and validity. British journal
of addiction, 78(2), 145-155.
Vinader-Caerols, C., Monleón, S., & Parra, A.
(2014). Physiological and
psychological effects of a high dose
of alcohol in young men and women.
Adicciones, 26(3), 238-246.
World Health Organization. (2001). The World
Health Report 2001: Mental health:
new understanding, new hope.
Conflict of interest: None
Role of funding source: None
Conflict of interest: None
Role of funding source: None


