Indian Journal of Health Social Work
(UGC Care List Journal)
Effects of Social Networking Sites on Students’ Psychosomatic Health in Western Odisha Universities During COVID-19 Pandemic - A statistical Analysis
Deepak Kumar Behera1, Rajendra Gartia2 & Hariom Pachori3
1,3Research Scholar & 2 Assistant Professor, School of Statistics, Gangadhar Meher University, Amruta Vihar, Sambalpur, Odisha- 768004, India
Correspondence: Rajendra Gartia, e-mail id: rajendra.gartia@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Background: Social networking sites, the driver of every minute information has established a tremendous pace among the youths. No doubt it has given a great platform for any individual to exchange ideas and grab information from worldwide. Smartphones and internet connections are all requirements, and everything is just with a click of a button. It has been observed that the younger generation is very much prone to social networking sites. Social media and students have developed such a bond that has resulted in numerous benefits, but every object has its pros. and cons. Social networking sites (SNSs) has both positive and negative impact on the day-to-day life of university students and that finally shows the consequences on their psychosomatic health and academic performance (AP) and academic life. Aim: This research study aims to examine how the COVID-19 outbreak influenced university students’ psychosomatic health issues in western Odisha. The investigation will focus on determining the most preferred social media platforms for university students in western Odisha and explore the effect of students’ dependence on social media and how it might be affecting their psychosomatic health. Methods and Materials: The study will be both qualitative and quantitative based on primary data collected through a questionnaire. The main purpose of this research is to explore and analyze the basic concept underlying social networking sites as well as their applicability, usage, and impact on students’ psychosomatic health. For ease of data comparison descriptive statistics, bar diagrams, pie charts, and frequency count were used were as to draw valid statistical inference about the population, testing of hypothesis, t-test, Man Whitney U test, Chi-square tests have been employed as valid statistical tools to achieve the desired objectives. Conclusion: The study reveals that the respondents mainly suffer from headaches, Anxiety, and Acidity by continuous use of social networking sites through mobile phones. WhatsApp is found to be the most preferred platform. The study also reveals that females are more susceptible to psychosomatic health diseases than their male counterparts and there exists a significant association between psychosomatic health and total time spent and active period on social networking sites.
Keywords: Covid-19 Pandemic, Social Networking Sites, Psychosomatic health, University student.
INTRODUCTION
Internet and Social Networking Sites (SNSs) have revolutionized communications to such an extent that it is now our preferred medium of everyday communication. In the 1980s and 1990s, the internet widened in scope to encompass the Information Technology (IT) capabilities of universities and research centers. The internet has become an indispensable part of today’s society. The emergence of web 2.0 in the first decade of the twenty-first century was itself a revolution in the short history of the internet and social networking sites, fostering the rise of social media and other interactive, crowd-based communication tools [1]. It has at once turned into a worldwide broadcasting mechanism for information dissemination, and a medium for collaboration and interaction between individuals and their computers without regard for geographic location. The population of adolescents is 253.2 million according to the census 2011 [2]. Psychosomatic means mind (psyche) and body (soma). Psychosomatic health or disorder is a disease that involves both mind and body. Some physical diseases are thought to be particularly prone to be made worse by mental factors such as sleeplessness (Insomnia) or sleeping disorder, stress, depression, anxiety, etc. For example, these include psoriasis, eczema, stomach ulcers, high blood pressure, and heart disease. The mental state can affect how bad a physical disease is at any given time. The Merri am-Webster dictionary define s psychosomatic as relating to, involving, or concerned with bodily symptoms caused by mental or emotional disturbance [3]. The COVID-19 pandemic has forced leaders in politics and at universities to take drastic measures that affect how students and citizens interact and socialize with each other. In many countries around the world, individuals are required to reduce physical contact with others outside their household (social distancing) (Lancet, 2020). Additional measures include curfews, quarantines, and the closing of non-essential stores, schools, and universities. As many universities suspended classroom teaching and switched to online teaching, the lives of students have changed drastically (Glass RJ, et al. 2006). While social distancing measures may successfully slow down the spread of the infection and relieve the public health systems, they may eventually increase the social isolation of students and affect their psychological well-being and psychosomatic health (Bavel JJV, et al. 2020). Being under a lot of pressure to perform academically, students are pro ne to developi ng psychosomatic health problems (Mikolajczyk RT, et al. 2008). The social networking sites of students have been argued to be an important factor in buffering stress and helping them to be more effective (Stadtfeld C, et al. 2019). Reduced social interactions, a lack of social support, and newly arising stressors associated with the COVID-19 crisis could po tentially affect students ’ psychosomatic health negatively. Adolescents spending more and more time on the internet and social networking sites (SNSs) are prone to restrict physical activities, obesit y, insomnia, nomophobia, eyesight-related problems, sleep deprivation, body aches, and many others. Students are one of the most important users of the virtual world and social networks. The overuse of social networks has positive and negative academic, social, and health consequences for students (Jha RK, et al. 2016). Reduced academic performance is one of the most important consequences of social networking overuse for students. The results of a study on medical students showed that students who used social networking sites and the internet more than average had poor academic achievement and level o f concentration in the classroom (Upadhayay N, Guragain S. 2017).
A. SNSs’s positive benefits on psychosomatic health:-
SNSs’ positive benefits on psychosomatic health include the fact that social networking has significantly changed culture and way of life.
The following is a summary of some of the advantages of social networking sites and how students profit from their psychosomatic health status:
- Reduced stress; Less physical sickness; Seeking or providing emotional assistance when necessary.
- If you live in a remote place, for instance, or have limited independence, social anxiety, or are a member of a disadvantaged group, find a crucial social connection.
- It Keeps in touch and up to date with relatives and friends all across the world. Include the fact that social networking has significantly changed culture and way of life.
Social networking has triggered a huge cultural and lifestyle transformation. Social networking sites have several negative impacts that affect students’ psychosomatic health, including the following:
- Because this generation is so new, little research has been done to determine the long-term effects of social media use, and whether they are beneficial or detrimental. But several studies have discovered a solid link between excessive use of social media and a higher risk of 2 1 EFFECTS OF SOCIAL NETWORKING SITES ON STUDENTS’ PSYCHOSOMATIC HEALTH IN WESTERN ODISHA UNIVERSITIES DURING COVID- 19 PANDEMIC – A STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Indian Journal of Health Social Work. 4(1) January-June, 2022 depression, anxiety, loneliness, self-harm, and even suicide ideation.
- Cyberbullying.
- Self-absorption.
- Being sidetracked at work or school; Lack of time for introspection; Sleep issues; Worsening of anxiety or depressive symptoms.
- Dangerous conduct to obtain likes, shares, or favorable comments on social media.
The purpose of the study is to examine how the COVID-19 outbreak influenced university students’ psychosomatic health issues in western Odisha. The investigation will focus on determining the most preferred social media platforms by university students in western Odisha, to explore the effect of students’ dependence on social media and how it might be affecting their psychosomatic health.
The following Null hypothesis and Alternative hypothesis are tested to arrive at the desired objectives:
- H00 = There is no discernible difference between males and females in terms of psychosomatic health issues.
- H01 = The prevalence of psychosomatic health issues in males and females differs significantly.
- H10 = Psychosomatic health is independent of Gender.
- H11 = Psychosomatic health depends on Gender.
- H20 = The overall number of hours spent on SNSs is unrelated to psychosomatic health.
- H21 = The overall number of hours spent on SNSs affects psychosomatic health.
- H30 = Psychosomatic health is independent of active time period on SNS
- H31 = Psychosomatic health depends on the active time period on SNS.
Participants and Procedure
Covid- 19 Social Media and Psychosomatic Health of Students Questionnaire “ (CSMAPHOSQ). During the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown, the covid- 19 Social 2 2 EFFECTS OF SOCIAL NETWORKING SITES ON STUDENTS’ PSYCHOSOMATIC HEALTH IN WESTERN ODISHA UNIVERSITIES DURING COVID- 19 PANDEMIC – A STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Indian Journal of Health Social Work. 4(1) January-June, 2022 Media and Psychosomatic Health of Students Questionnaire “ (CSMAPHOSQ) was created specifically to measure University students’ perceived psychosomatic health problems due to using social networking sites during the period of covid- 19 pandemic. Research technique is the broad strategy or procedure used to help the study accomplish its specific goals and objectives. It states that the issue under examination has been thoroughly investigated and dealt with. As a result, the study is more thorough and effective. Research design, data collection, reliability and validity, data analysis, and ethical issues that come up throughout the research process are all examples of study procedures.

 From graph 2 it is found that the mean rank
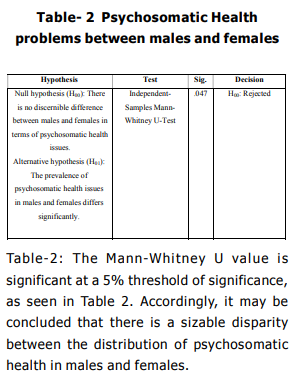
From graph 2 it is found that the mean rank
of females (148.33) is higher than the mean
rank for males (129.32). So, it may be
inferred that females are more susceptible to
psychosomatic health diseases than their male
counterparts. To ascertain this claim, a MannWhitney U -test for independent samples is
done and the result is presented in table 3.
DISCUSSION
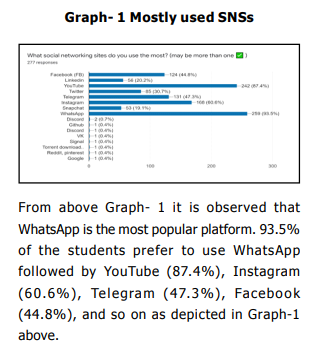
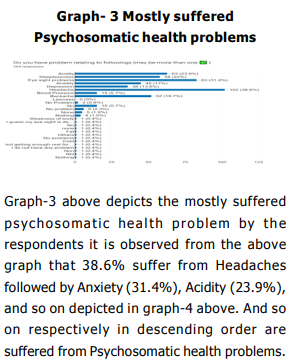
 Students who use SNSs more frequently are more likely to be unwell. Their health, social interactions, and s leep quality are all negatively impacted by increased SNS usage, which also promotes a sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity, all of which increase their risk of developing non-communicabl e Psychosomatic health issues. It is observed that WhatsApp is the most popular platform i.e., 93.5% of the students prefer to use WhatsApp followed by YouTube (87.4%), Instagram (60.6%), Telegram (47.3%), and Facebook (44.8%), and so on as depicted. The result reveals tha t females are more susceptible to psychosomatic health diseases than their male counterparts. From the statistical investigation, we have found that the mean rank of females (148.33) is higher than the mean rank for males (129.32). Thus, it may be inferred that there exists a significant difference in the distribution of Psychosomatic Health between males and females. The analysis depicts that 38.6% suffer from Headaches followed by Anxiety (31.4%), Acidity (23.9%). From the analysis, we find that the psychosomatic health problems significantly depend on the total hours spent using social networking sites (SNS) (p<0.05). Because of SNSs, they are unable to know all the important information, news, ideas, skills, etc. happening around the world. Evidence suggests that individuals may experience symptoms of psychosis, anxiety, trauma, suicidal thoughts, and panic attack (WHO, 2020) due to the use of SNSs during the covid- 19 period. Covid-19 has also been proven to improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, sadness, and post-traumatic stress symptoms in recent research (Ahmed et.al.2020).
Students who use SNSs more frequently are more likely to be unwell. Their health, social interactions, and s leep quality are all negatively impacted by increased SNS usage, which also promotes a sedentary lifestyle and physical inactivity, all of which increase their risk of developing non-communicabl e Psychosomatic health issues. It is observed that WhatsApp is the most popular platform i.e., 93.5% of the students prefer to use WhatsApp followed by YouTube (87.4%), Instagram (60.6%), Telegram (47.3%), and Facebook (44.8%), and so on as depicted. The result reveals tha t females are more susceptible to psychosomatic health diseases than their male counterparts. From the statistical investigation, we have found that the mean rank of females (148.33) is higher than the mean rank for males (129.32). Thus, it may be inferred that there exists a significant difference in the distribution of Psychosomatic Health between males and females. The analysis depicts that 38.6% suffer from Headaches followed by Anxiety (31.4%), Acidity (23.9%). From the analysis, we find that the psychosomatic health problems significantly depend on the total hours spent using social networking sites (SNS) (p<0.05). Because of SNSs, they are unable to know all the important information, news, ideas, skills, etc. happening around the world. Evidence suggests that individuals may experience symptoms of psychosis, anxiety, trauma, suicidal thoughts, and panic attack (WHO, 2020) due to the use of SNSs during the covid- 19 period. Covid-19 has also been proven to improve mental health outcomes such as anxiety, sadness, and post-traumatic stress symptoms in recent research (Ahmed et.al.2020).
CONCLUSION
The authors are grateful to all the participants who took part in this research. I also owe a great deal of love and gratitude to my guide, family members, and friends
Role of funding source: None

ISSN: 2582-1393 (online)
UGC Care List Journal

